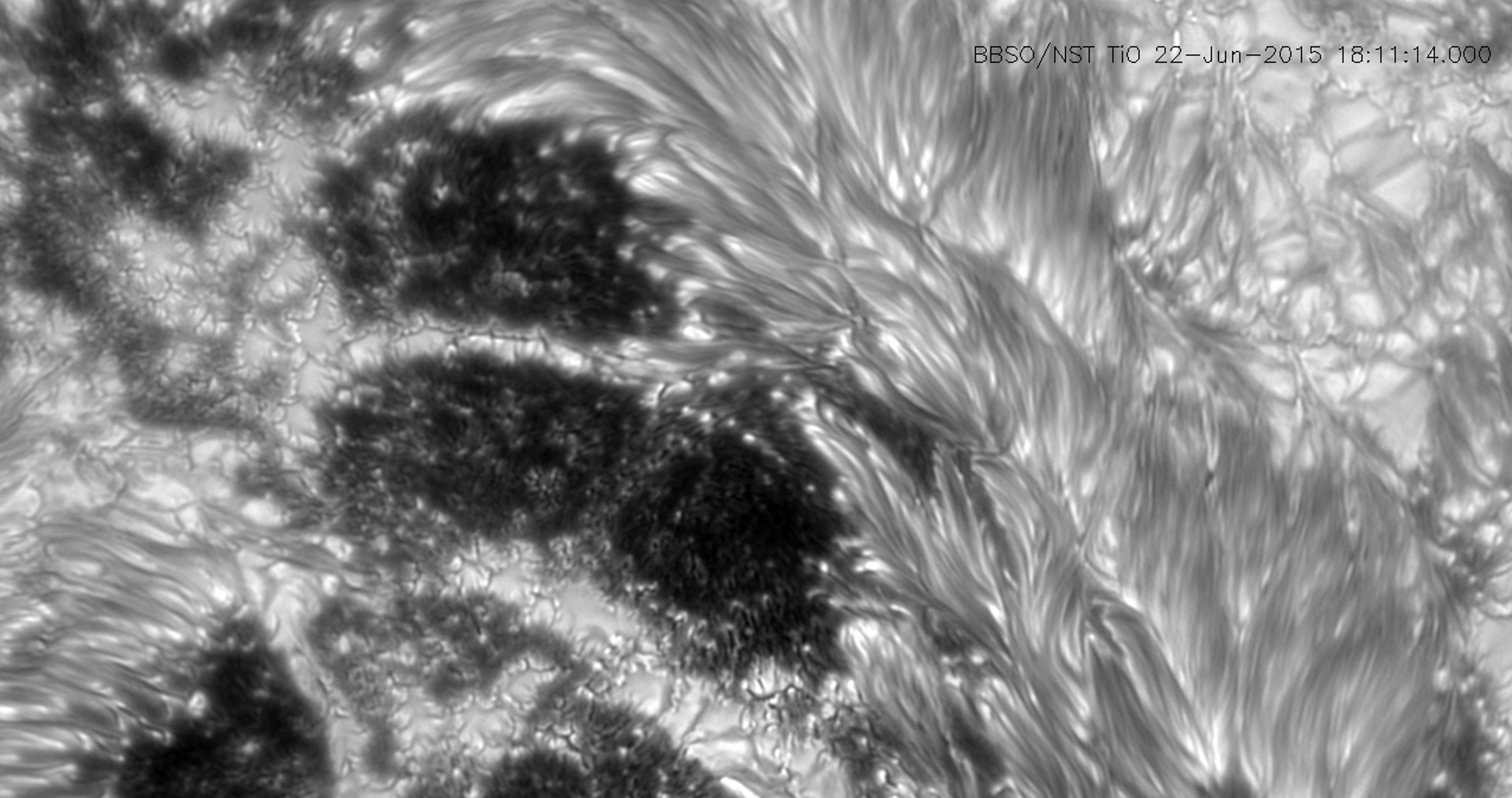
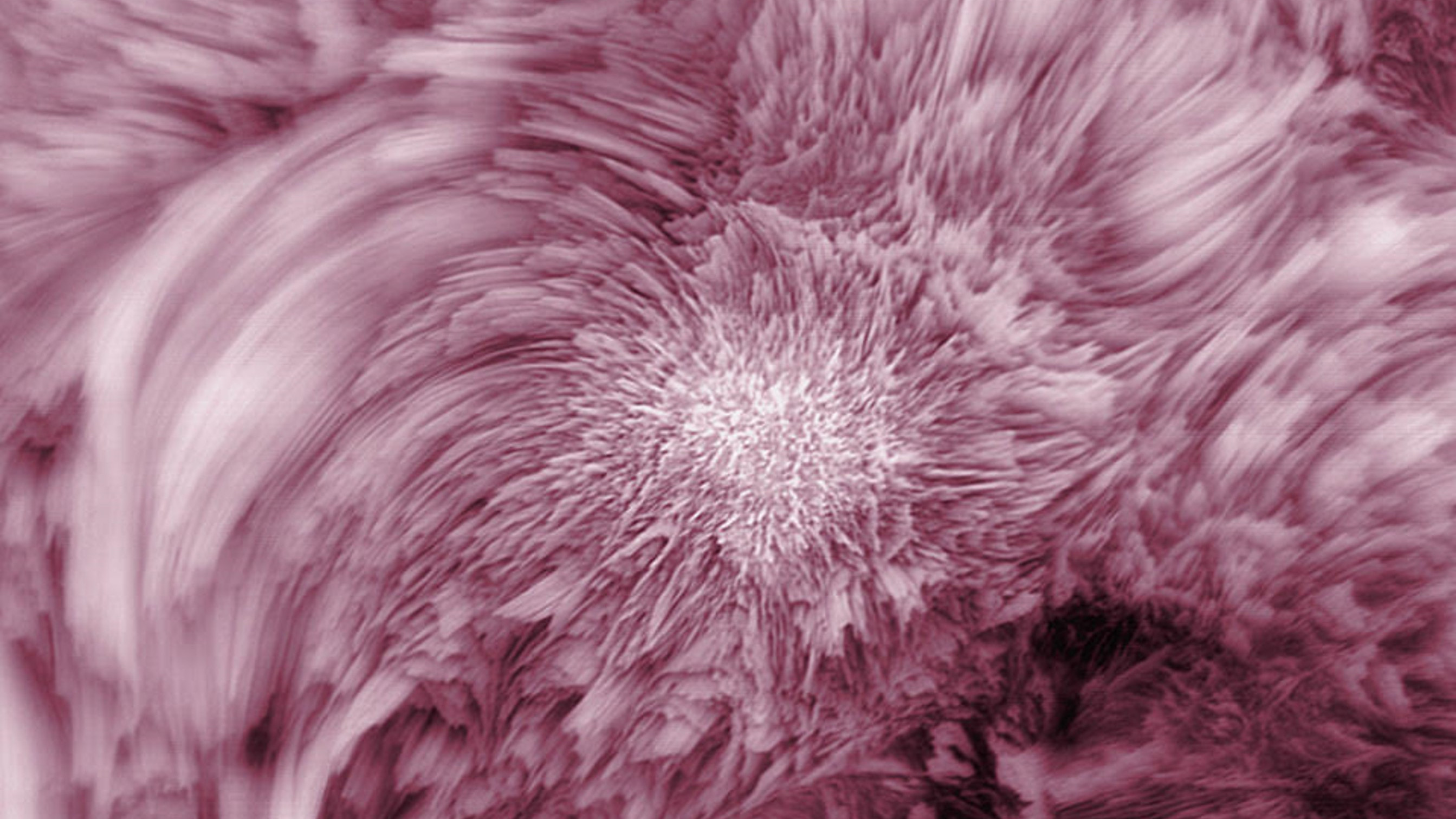
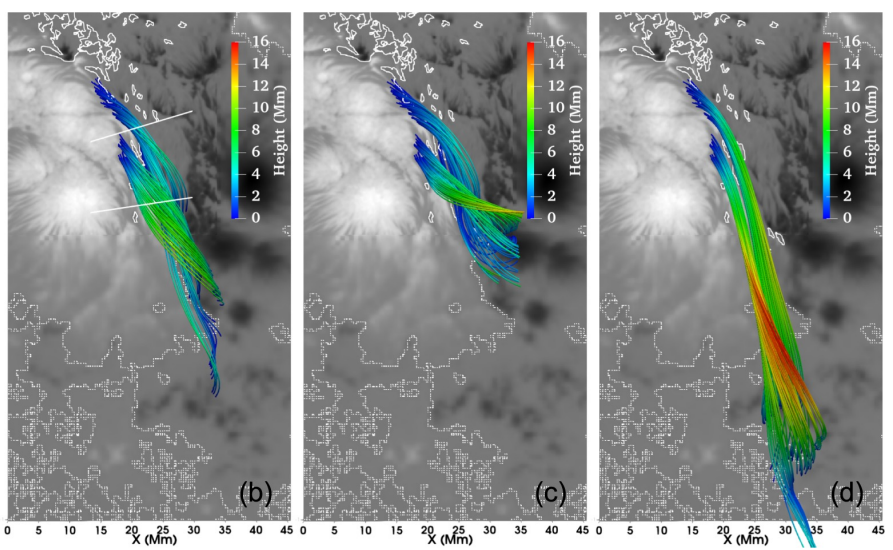
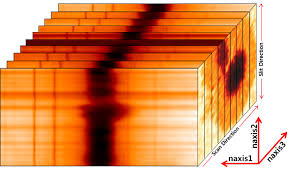
BBSO exploits the excellent climatic conditions of Big Bear Lake to study the Sun, source of life on Earth. The observatory is located in the middle of Big Bear Lake to reduce the image distortion which usually occurs when the Sun heats the ground and produces convection in the air just above the ground. Turbulent motions in the air near the observatory are also reduced by the smooth flow of the wind across the lake instead of the turbulent flow that occurs over mountain peaks and forests. These conditions, combined with the usually cloudless skies over Big Bear Lake and the clarity of the air at 2,000 meters (6,750 feet) elevation, make the observatory a premier site for solar observations.
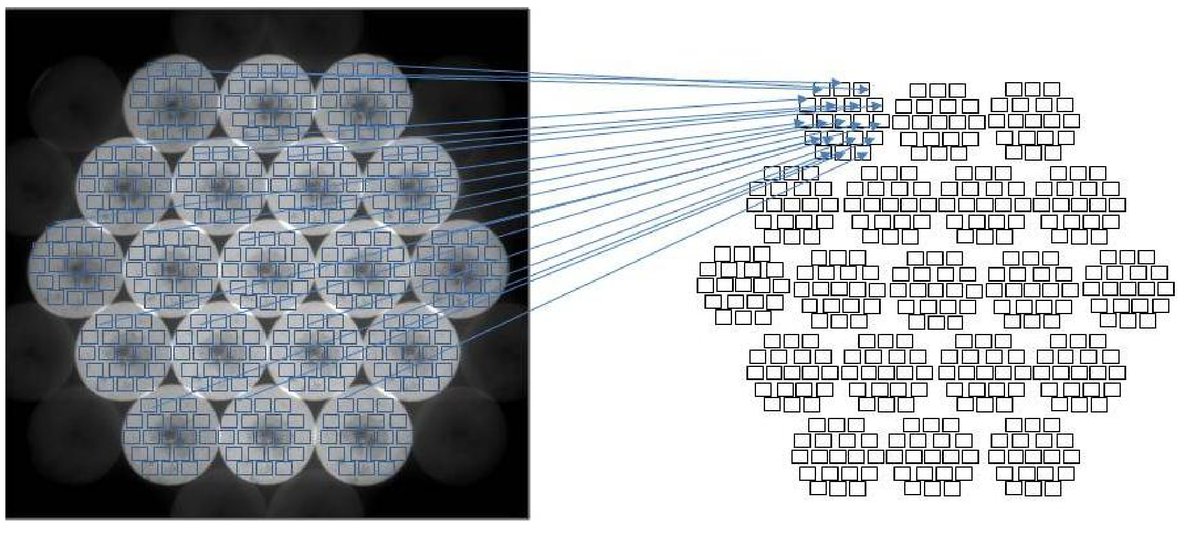
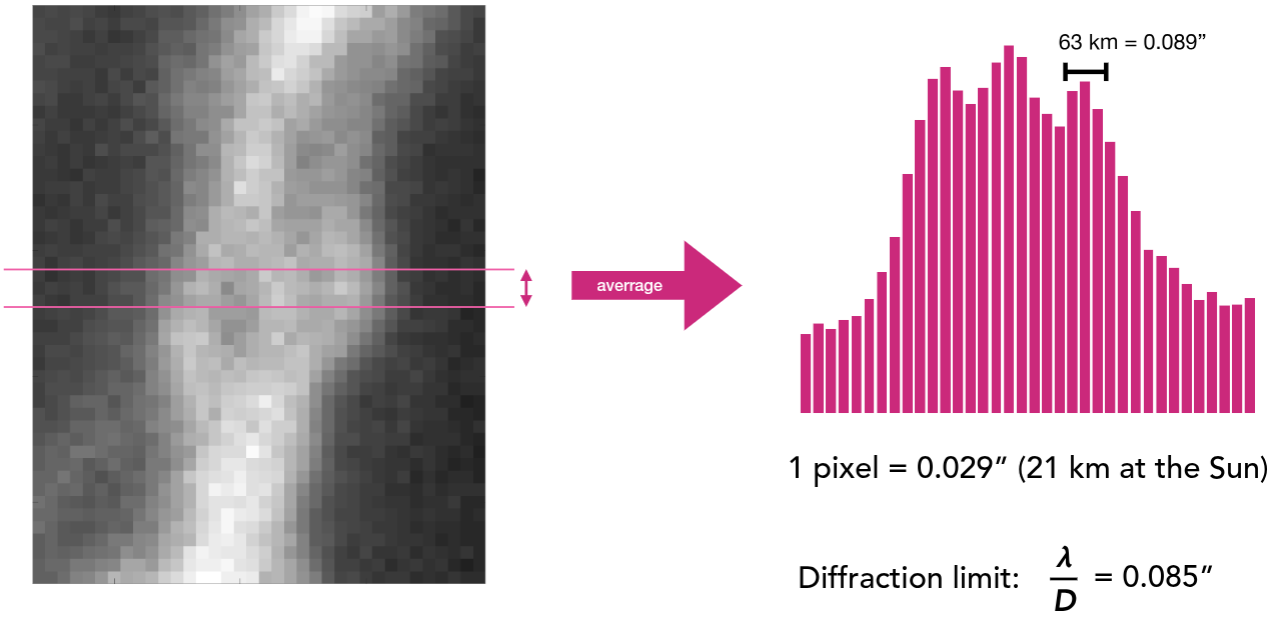
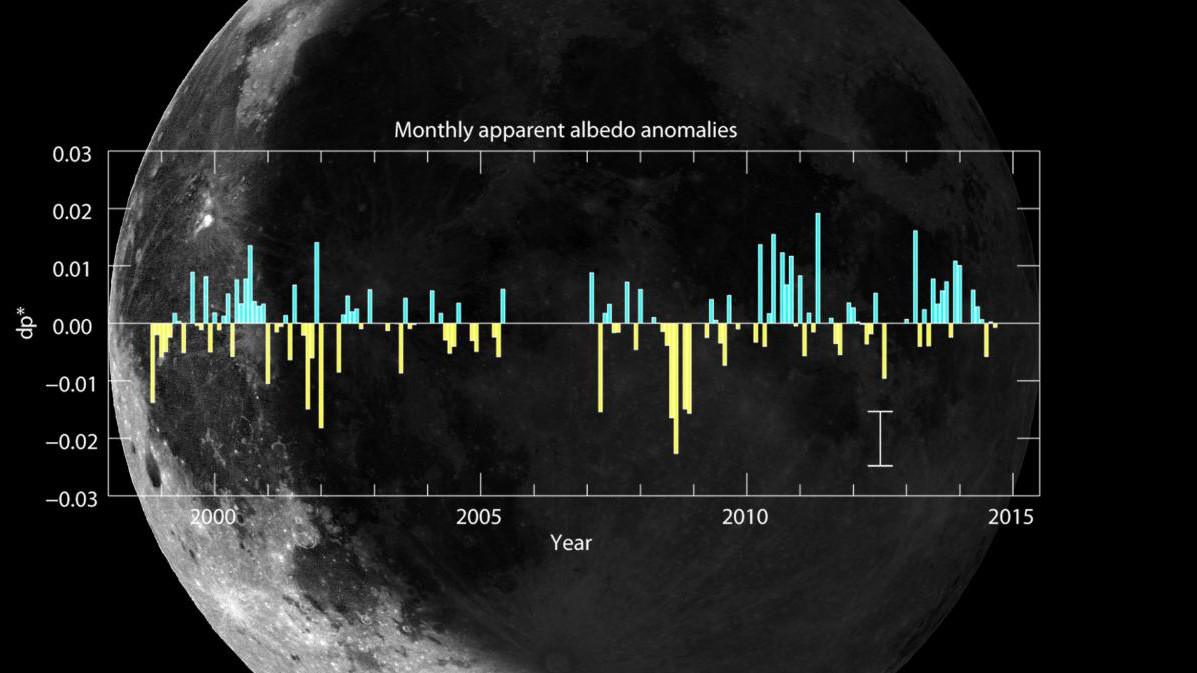
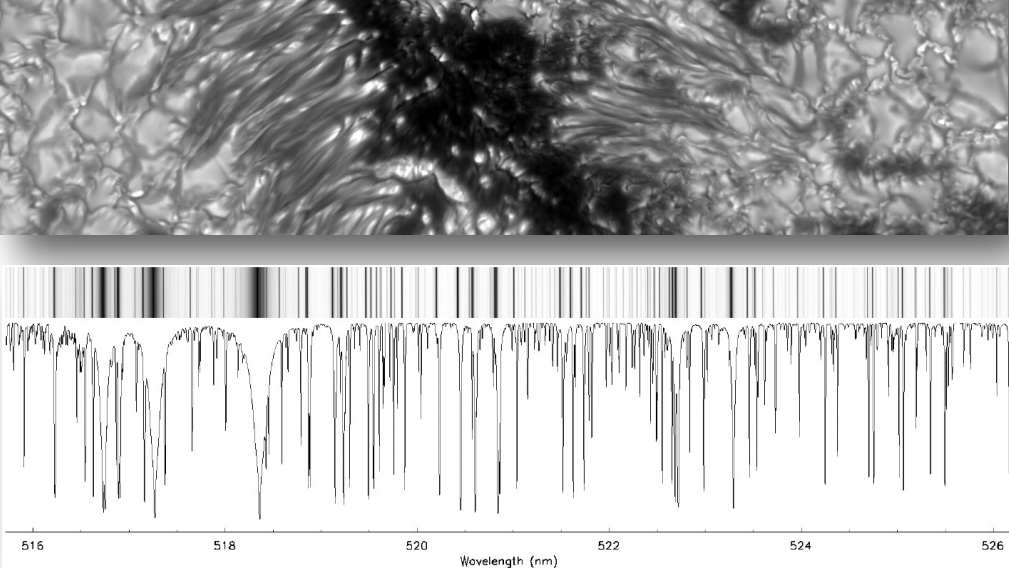
BBSO is the site of the high-order adaptive-optics (AO) corrected GST and its post-focus instrumentation, which consists of i) a broadband filter imager — BFI; ii) visible imaging spectrometer — VIS; iii) near-infrared imaging spectropolarimeter — NIRIS; iv) fast-imaging solar spectrograph — FISS; and v) a cryogenic infrared spectrograph — Cyra).
BBSO instrumentation is described in a number of publications, available here.
Also on the site is an H-alpha full-disk imager, a Global Oscillations Network Group (GONG ) station, and NSO SOLIS facility.